√100以上 epimysium perimysium endomysium histology 115161-Epimysium perimysium endomysium histology
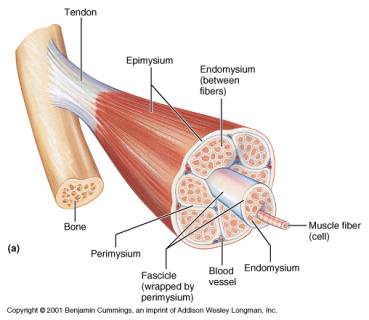
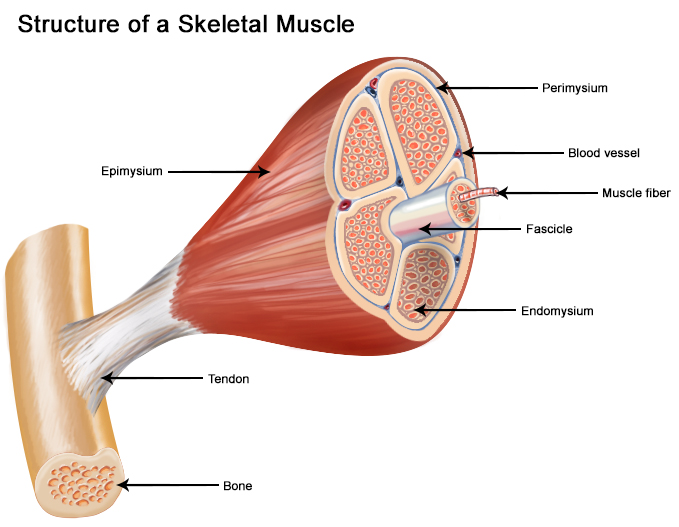
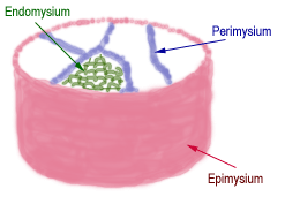
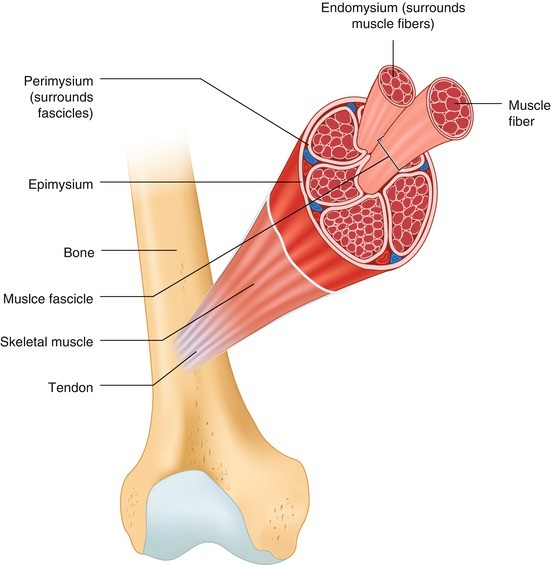
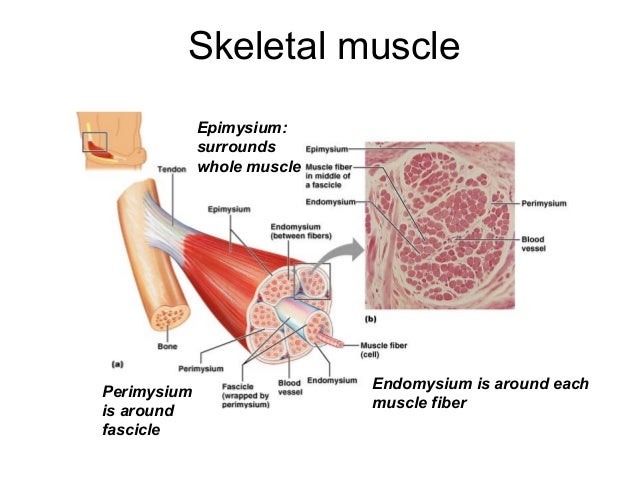
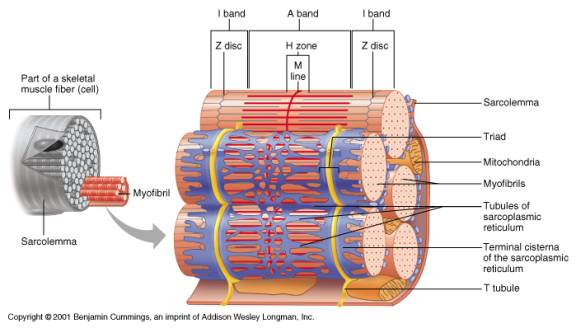
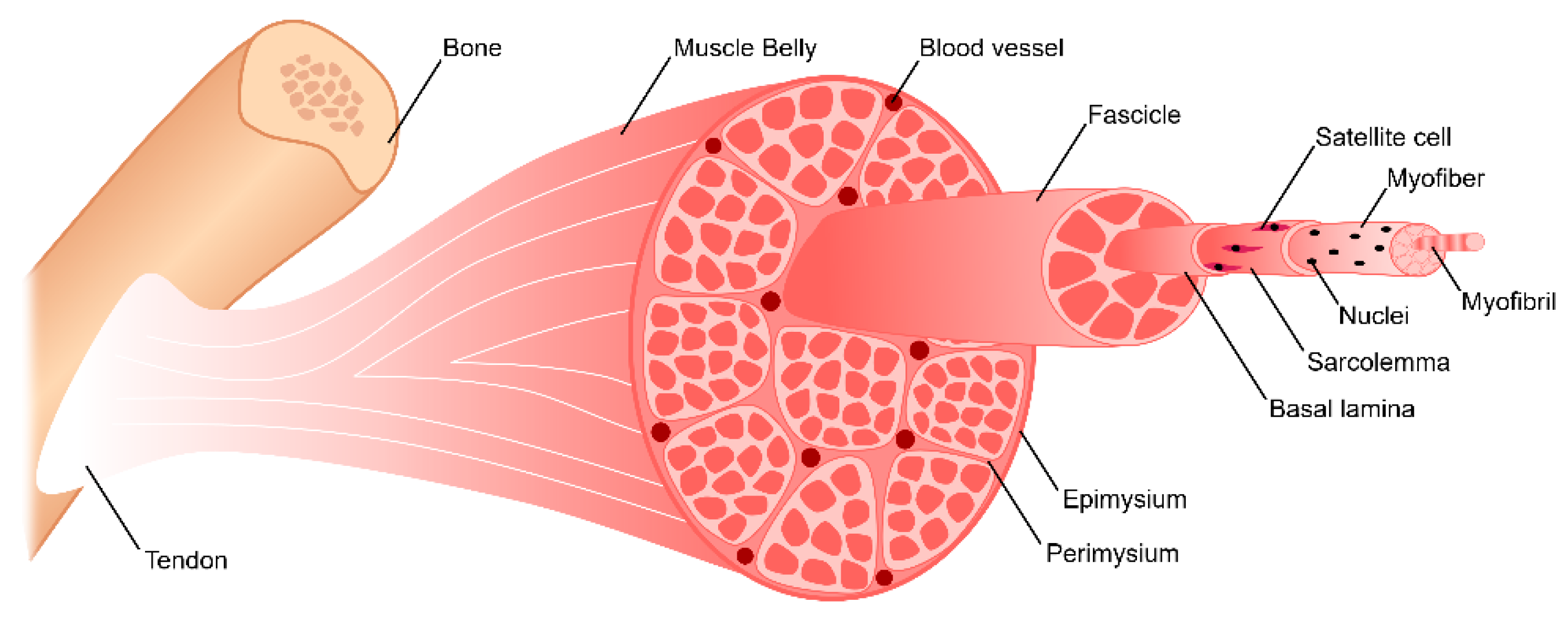
(2) separate the muscle into compartments; The most superficial layer of a muscle is the epimysium which wraps together numerous fascicles wrapped with perimysium Inside each fascicle are the individual muscle fibers wrapped around endomysium Within the muscle fibers is where the functional unit of the fiber exists the sarcomereHowever, the thickness and constitutent connective tissue fiber types of these sheaths varied regionally Near the articular capsule and disc, the endomysium, perimysium, and
Histology Of Muscle
Epimysium perimysium endomysium histology
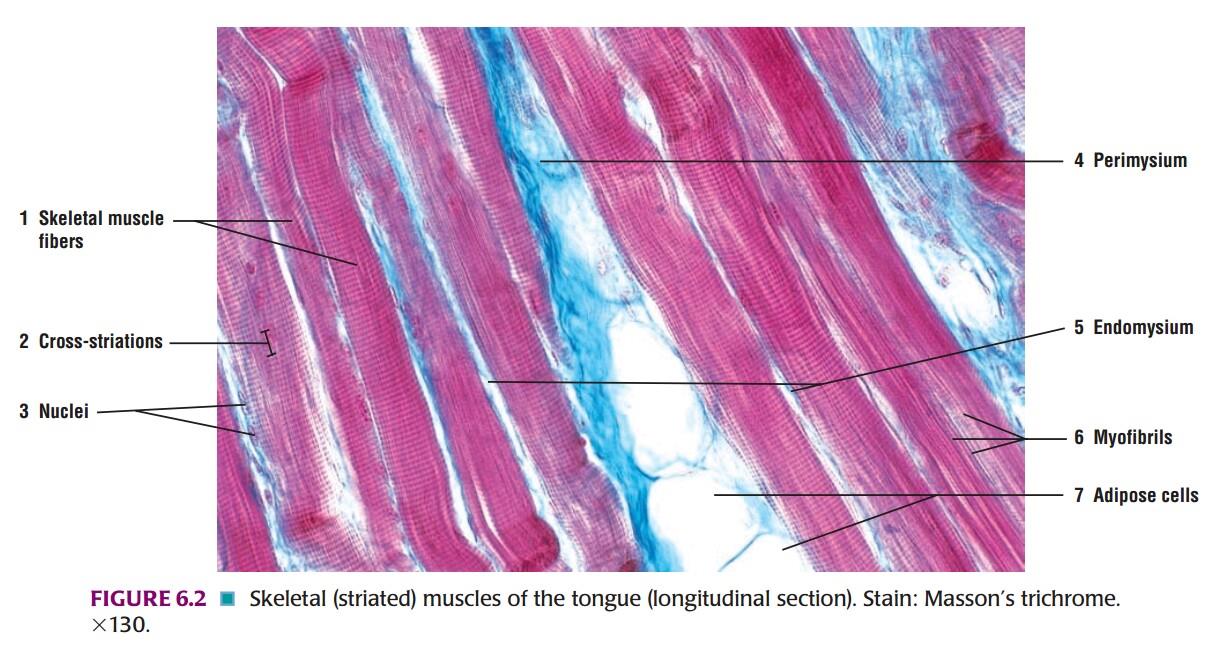
Epimysium perimysium endomysium histology-Perimysium encloses groups of fibers, defining fasciclesThis is a section of the tongue Begin by identifying groups of fasciculi cut in transverse section Where are the nuclei located within a cell?




Muscles Bioactive Collagen Peptides
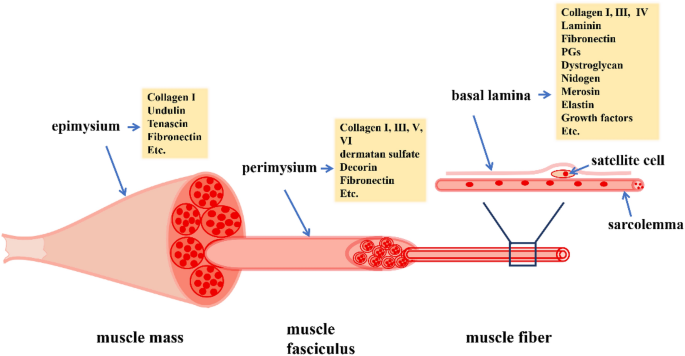
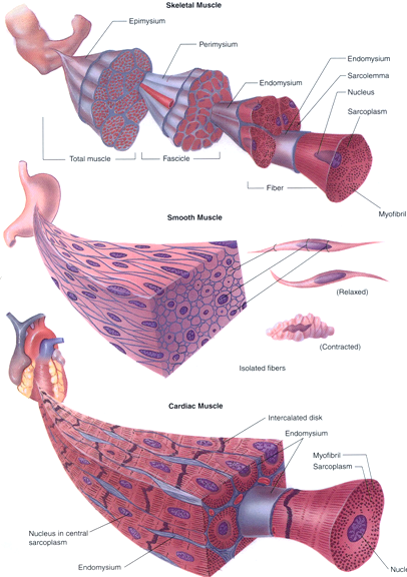
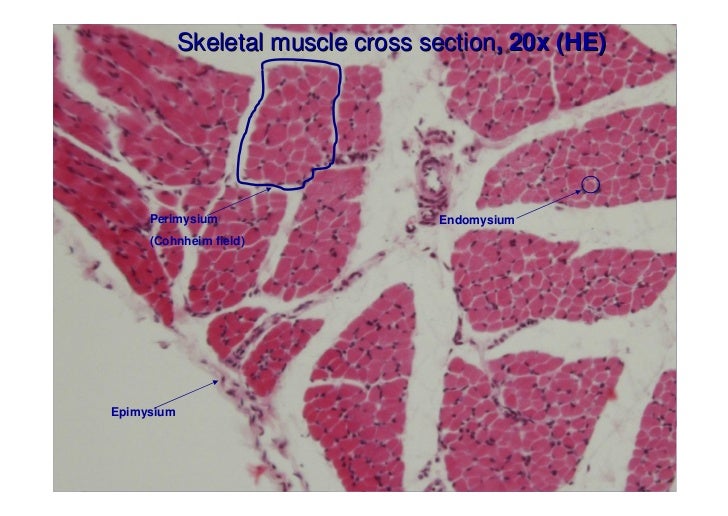
The whole muscle is enclosed by a dense connective tissue sheath called the epimysium (Epi greek for upon, mys greek for muscle) The muscle fibres are divided up into bundles of fibres called 'fascicles' Fibrous sheaths that surround the fascicles are called the perimysium (peri is greek for around) Blood vessels, the lymphatics and the nerves are all found in the perimysiumEpimysium is the specialized fascia located at the muscle Epimysium is a layer of connective tissue, which ensheaths the entire muscle It is composed of dense irregular connective tissue It is continuous with fascia and other connective tissue wrappings of muscle including the endomysium, and perimysium 1From the epimysium, thin collagenous septa extend inward to divide the muscle into a number of bundles or fasciclesThese septa are called the perimysium The perimysium is continuous with the endomysium that is a delicate connective tissue layer surrounds each individual myofibers
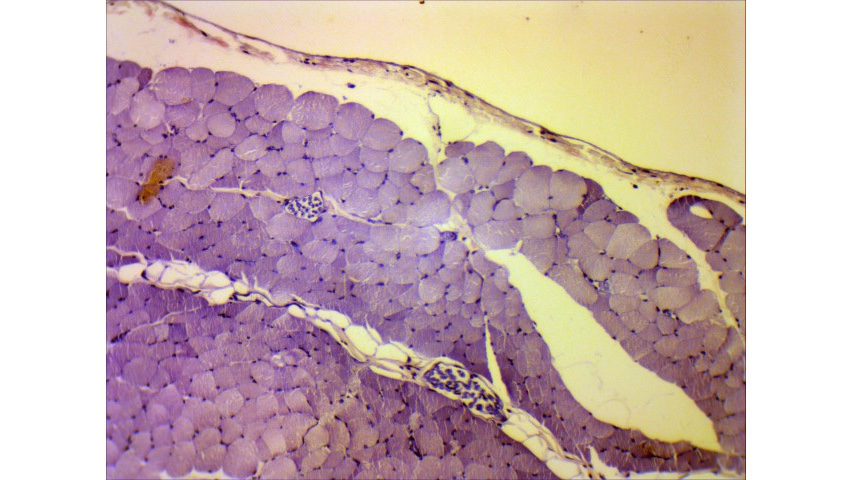
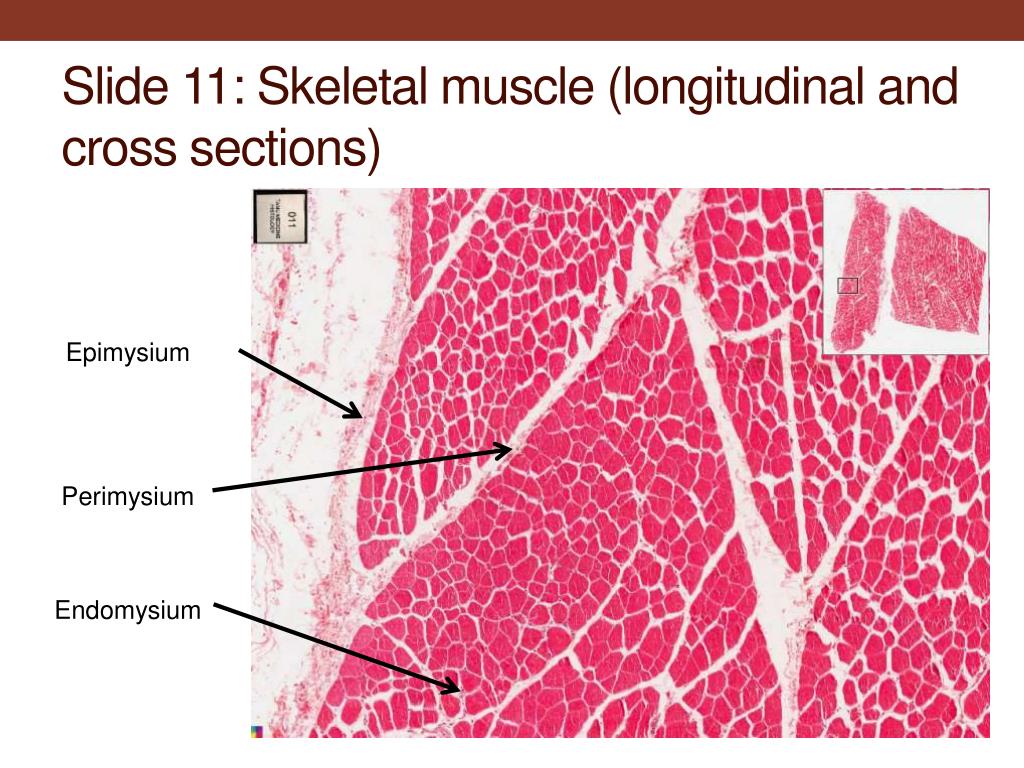
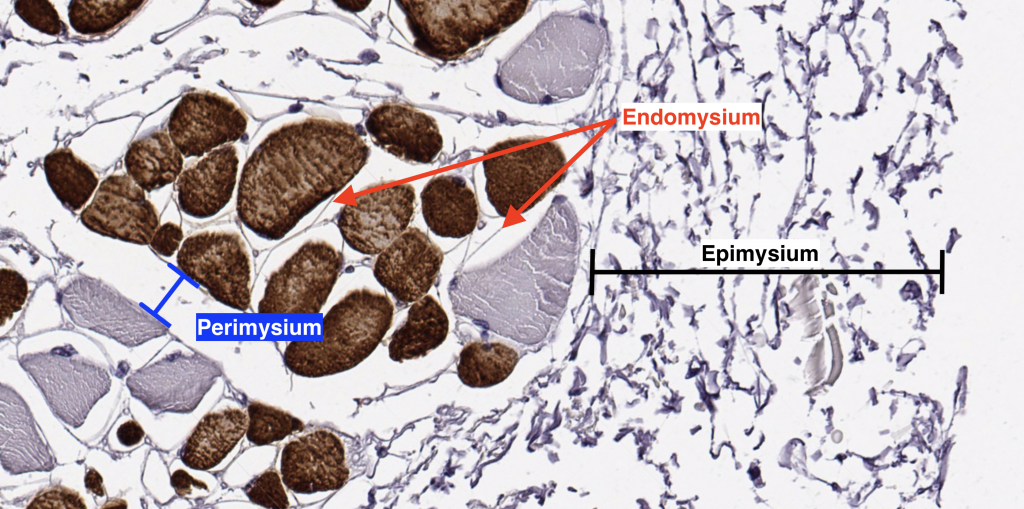
Groups of these fibrils form a muscle fiber, which is surrounded by endomysium Muscle fiber and muscle cell are synonymous Groups of individual cells that are surrounded by perimysium are known as fascicles and groups of these fascicles, surrounded by epimysium make up a muscle B Perimuscular Connective Tissue Here you will easily identify the epimysium, perimysium and endomysium of skeletal muscle fibers You will also find the ovoid nuclei in the skeletal muscle fascicles at the periphery Muscle slide images and videos I think these labeled images and diagrams of skeletal muscle histology were helpful to understand the basics of this muscle structure 1) Each muscle fibres is surrounded by delicate connective tissue that is called the endomysium 2) Individual fasciculi are enclosed by a stronger sheath of connective tissue called the perimysium 3) The entire muscle is surrounded by connective tissue called the epimysium This is illustrated by the schematic diagram below
Where can capillaries be found?The epimysium, perimysium and endomysium are noncontractile elements of a contractile tissue (muscle) Tendons are noncontractile, so they can be regular, because the tissue does not need to alter its length (in fact, for efficient function, a tendon should be as nonstretchy as possible)About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




Reading Php Lab



Animal Tissues Muscle Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
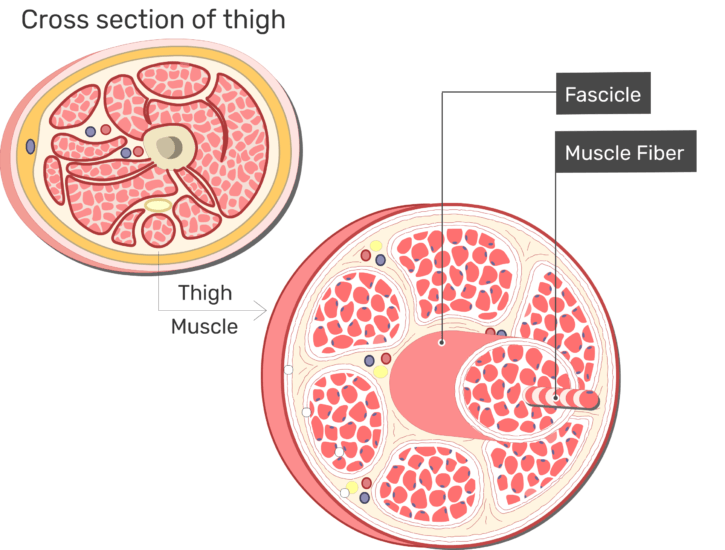
Epimysium A skeletal muscle is invested by three connective tissue layers that (1) bind the muscle together;The endomysium and perimysium were relatively thin and consisted mainly of reticular fibers The epimysium was thicker than the intramuscular sheaths and consisted of both collagen and reticular fibers;Anatomical terminology Perimysium is a sheath of connective tissue that groups muscle fibers into bundles (anywhere between 10 and 100 or more) or fascicles Studies of muscle physiology suggest that the perimysium plays a role in transmitting lateral contractile movements




How Muscle Structure And Composition Influence Meat And Flesh Quality



Seer Training Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
Can you identify the endomysium and the perimysium?Identify epimysium and perimysium With the 40X objective, examine muscle fibers cut in transverse and in longitudinal section and identify endomysium and blood vessels of various sizes (Figs 103 and 104) Where are the nuclei of these muscle fibers located?And (3) transmit the force of contraction to the muscle insertion Endomysium surrounds individual muscle cells;




Skeletal Muscle A 19 Diaphragm A 56 Muscle Skeletal Hmn Adult Ls A 57 Muscle Skeletal Fetal Ls Striation Large Elongate Cell Many Peripheral Nucleus Endomysium Ppt Download




Muscles Bioactive Collagen Peptides
How does the location of capillaries inThe mean strain for repairs with epimysium (104%) was significantly higher (p < 0001) than that for repairs without epimysium (73%) The mechanisms of failure were also different Among epimysium repairs, 15 stitches avulsed muscle transversely, and 10 stitches tore out longitudinally from the muscle In the nonepimysium group, 1 sutureE perimysium collagenous connective tissue that separates smaller bundles of muscle cells called fascicles F fascicle bundle of muscle cells bounded by perimysium G endomysium thinner layer of connective tissue that separates individual muscle cells III Skeletal muscle




Muscle Histology Ssn October 17 05 Presented By Tabassum Sardharwala Shannon Watkins Ppt Download




Muscle Tissue This Resource Is Licensed Under The Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial No Derivative Works License Ppt Download
The interstitial connective tissue of muscle is subdivided into the epimysium (surrounds the entire muscle), perimysium (surrounds large angular fascicles divided into primary fascicles of 10–100 fibers), and endomysium (surrounds individual muscle fibers) The endomysium contains capillaries, nerve fibers, fibroblasts, and collagen fibrilsNear the articular capsule and disc, the endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium were all thicker than in other regions of the muscle and consisted of collagen, reticular, and elastic fibers




The Muscular Force Transmission System Role Of The Intramuscular Connective Tissue Journal Of Bodywork And Movement Therapies




Perimysium Histology Kcpc Org




Introduction To Mussels Human Anatomy Physiology I Dr
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13584/skeletal-muscle-tissue_english.jpg)



Skeletal Muscle Tissue Histology Kenhub



Extracellular Matrix An Important Regulator Of Cell Functions And Skeletal Muscle Development Cell Bioscience Full Text




Home Php Lab



Muscle The Histology Guide



General Histology 2 Emedicodiary




Skeletal Muscle Consists Of Muscle Fibers Bound By Connective Tissue Download Scientific Diagram



X11 Histology Of Muscle Tissue Flashcards Chegg Com




Reading Php Lab




Muscle Fascia And Force Transmission Journal Of Bodywork And Movement Therapies



Muscle Tissue




Epimysium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Skeletal Muscle Histology Draw It To Know It



Skeletal Muscle Fiber Location And Arrangement



Histology Slides 1



1



Musculoskeletal System Springerlink




Diversity Of Extracellular Matrix Morphology In Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle Sleboda Journal Of Morphology Wiley Online Library
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/perimysium/ECXt7gUxRQFYokz6VI7Cw_Perimysium.png)



Perimysium Histology Modernalternativemama Com



Solved Label A Fascicle Perimysium Epimysium Chegg Com




Muscle



What Are The Epimysium Perimysium And The Endomysium Quora




Muscular System By Dr Shivarama Bhat Objectives To



1




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Animalscience Tamu Edu




I Heart Histo F Is For Fascicle A Snuggle Of Cells Wrapped Up In A Connective Tissue Coat In Peripheral Nerves Fascicles Of Axons Are Surrounded By A Peri Neurium Coat




Perimysium Definition Anatomy




Mitochondria Again But This Time In Muscle The Ms Blog



Skeletal Muscle Physiology




Medicine Hack Endomysium Perimysium And Epimysium Definition Histology



Muscle Histology By Dr Armaan Singh




Muscle




Histology Practical Musculoskeletal Block Things You Need To



Histology Of Muscle




Histology 4000 Muscle Lecture Notes 6



Bioengineering Free Full Text Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering Biomaterials Based Strategies For The Treatment Of Volumetric Muscle Loss Html



Ppt Muscle Tissue Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Cartilage Bone Muscle Histology Notes Medical Histology Jacobs School Of Medicine




Epimysium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Solved 1 1 N Oa 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Blood Vessel Chegg Com



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com



What Is The Difference Between Epimysium And Fascia Quora




Histology Of Muscle



Fascicle
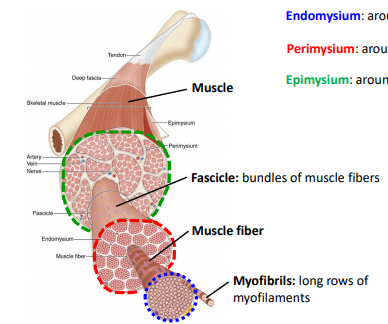



Histology Exam 2 Other Lectures




Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture 3 Lab Notes Quiz 3 Oneclass
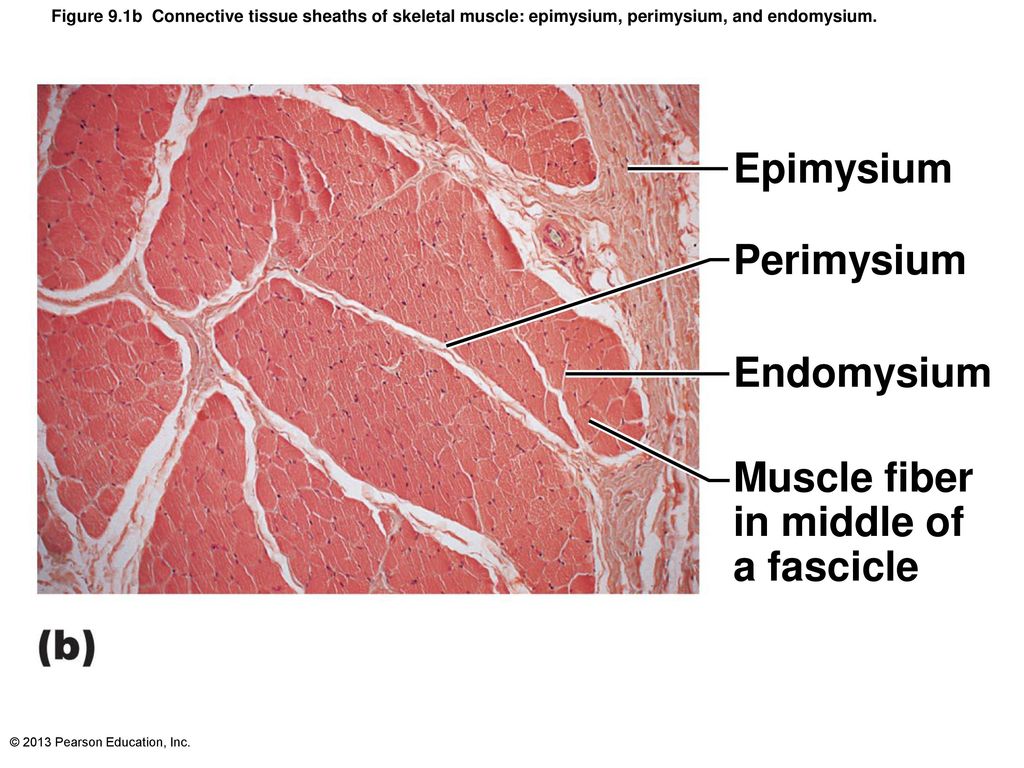



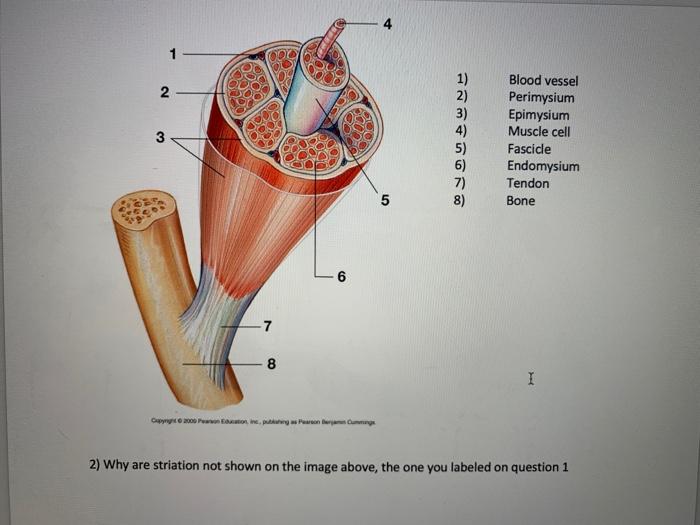
Chapter Opener 9 C 13 Pearson Education Inc Ppt Download




Endomysium Wikipedia




Skeletal Muscles Histology Fascicle Whole Muscle Muscle Fiber




4 Myofibril Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock



Muscle Tissue Sections




Histology Skeletal Muscle Epimysium Fascicle Of Muscle Cells Skeletal Muscle Medical School Muscle




Warm Up 1 Based On What You Know About Latin Root Words What Do You Think These Terms Refer To Sarcomere Sarcoplasm Myofibril Epimysium Perimysium Ppt Download
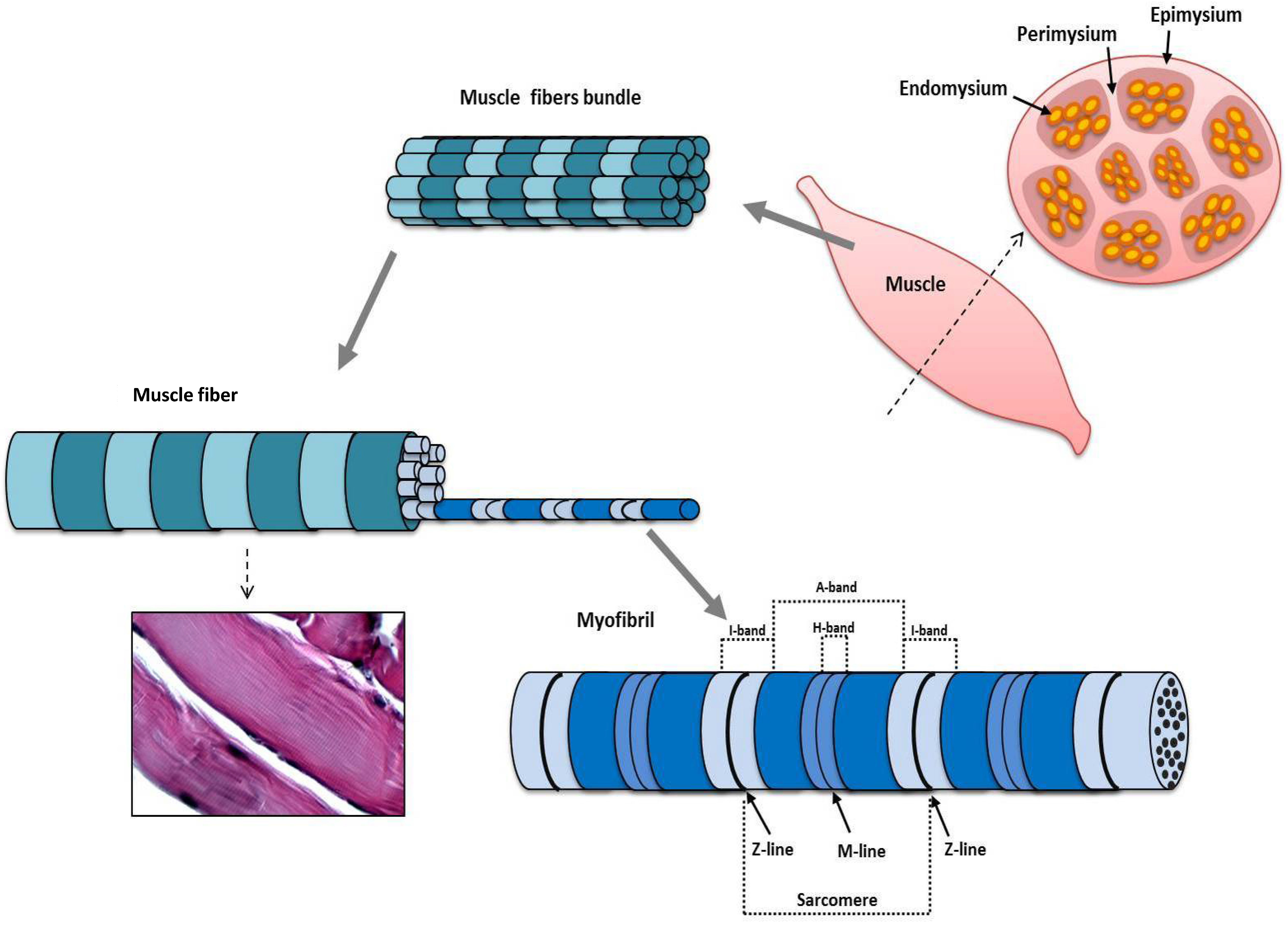



Jfmk Free Full Text Morphological And Functional Aspects Of Human Skeletal Muscle Html




Schematic Overview Of The 3 Components Of The Cardiac Interstitial Download Scientific Diagram




Chapter 9 Figure 9 1 Connective Tissue Sheaths Of Skeletal Muscle Epimysium Perimysium And Endomysium Diagram Quizlet



Histology Website Resource Ha9




What Is Muscular Tissue Histology Anjani Mishra




Human Muscle Epimysium Perimysium And Endomysium Muscular System Skeletal Muscle Muscle




Epimysium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Medicine Hack Endomysium Perimysium And Epimysium Definition Histology



1




Epimysium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Perimysium Histology Modernalternativemama Com
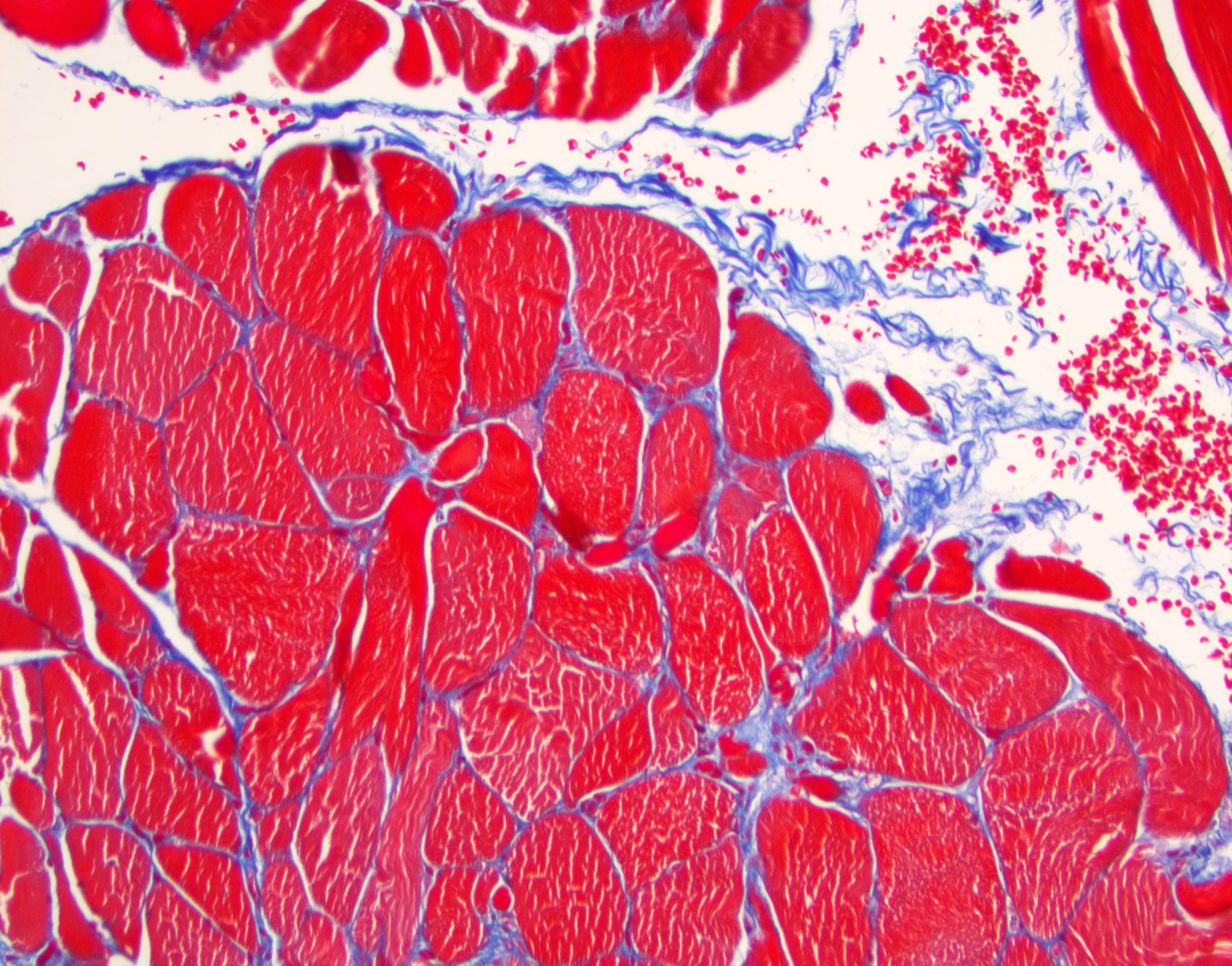



Pathology Outlines Histology Skeletal Muscle




Histology Of Muscle




Muscle
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1186/YdTKKcsV7yJfzybtC3TNXA_histology-motor-unit_English.png)



Skeletal Muscle Tissue Histology Kenhub




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Medicine Hack Endomysium Perimysium And Epimysium Definition Histology
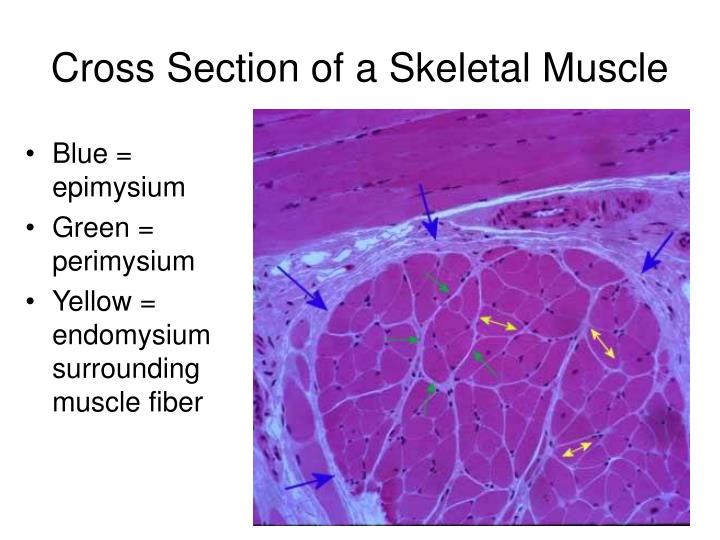



Ppt Muscle Histology Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
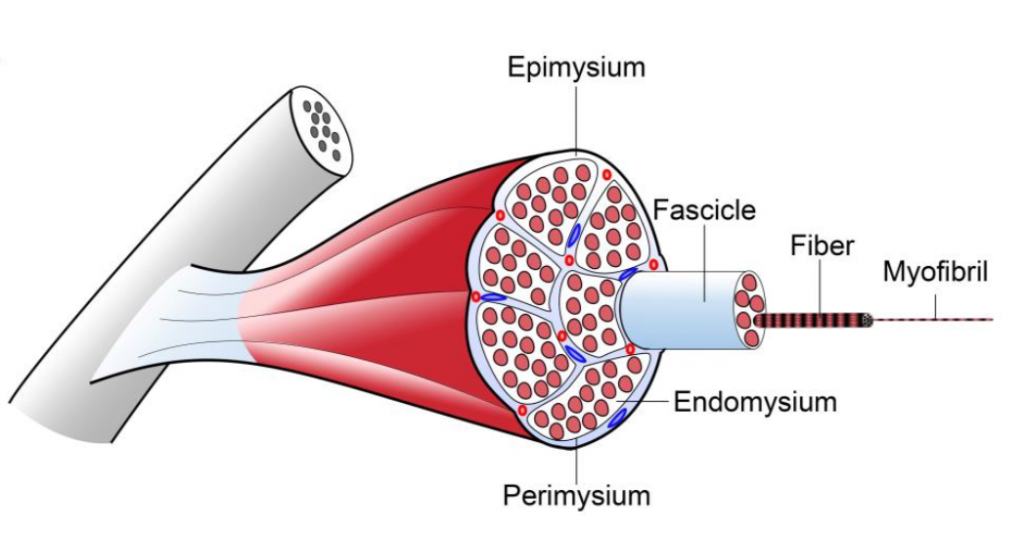



Cartilage Bone Muscle Histology Notes Medical Histology Jacobs School Of Medicine




Medicine Hack Endomysium Perimysium And Epimysium Definition Histology




Muscle Tissue Petr Vanhara Phd Dept Histology Embryology Ppt Download
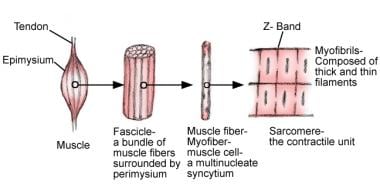



Skeletal Muscle Structure And Histology Overview Myofiber Types Histology Of Normal Skeletal Muscle




Medicine Hack Endomysium Perimysium And Epimysium Definition Histology



Vetmed Tamu Edu
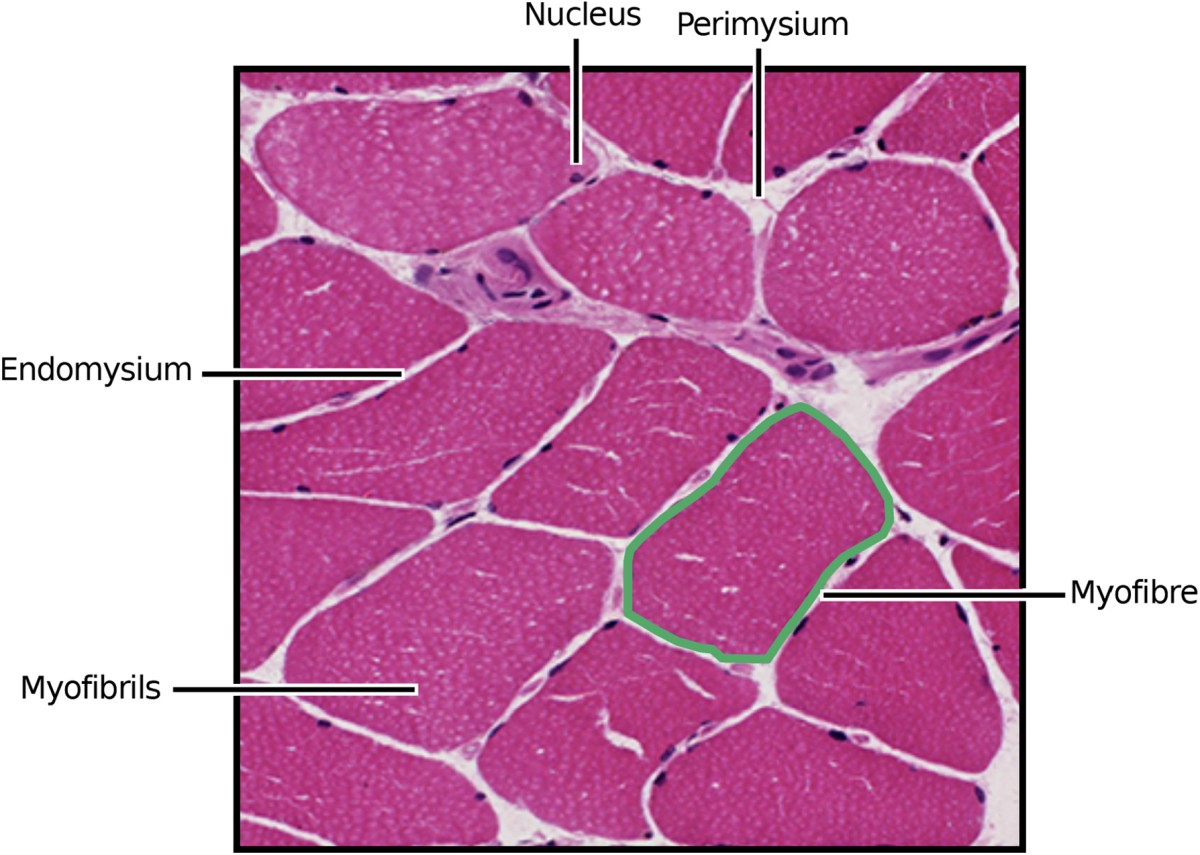



Myofibre Segmentation In H E Stained Adult Skeletal Muscle Images Using Coherence Enhancing Diffusion Filtering Bmc Medical Imaging Full Text



Muscle Tissue Sections




Normal Histology




Muscle Skeletal Muscle Transverse Cut A B C D A Epimysium B Perimysium C Endomysium D Fascicle Ppt Download



Sokvetjournal Net
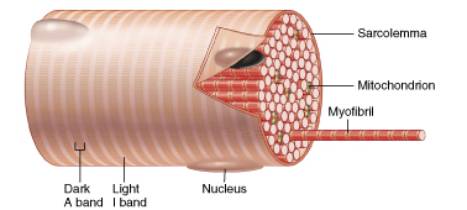



Histology Of Muscle




Skeletal Muscle Histology Slide Identification And Labeled Diagram Anatomylearner The Place To Learn Veterinary Anatomy Online




Histology Muscle Flashcards Quizlet




Epimysium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
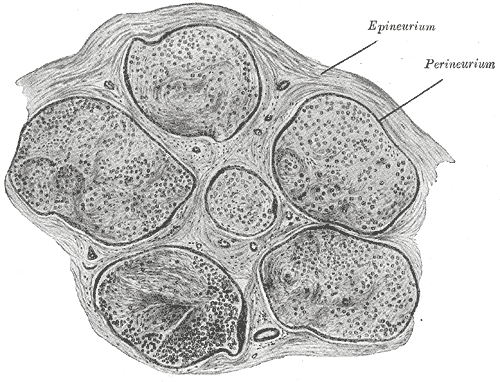



Perineurium Wikipedia




Muscle Histology Youtube




Schematic Diagram Showing Arrangement Of Extracellular Matrix Ecm In Download Scientific Diagram




Usmle Anatomy Chapter 4 Muscle Tissue Flashcards Quizlet
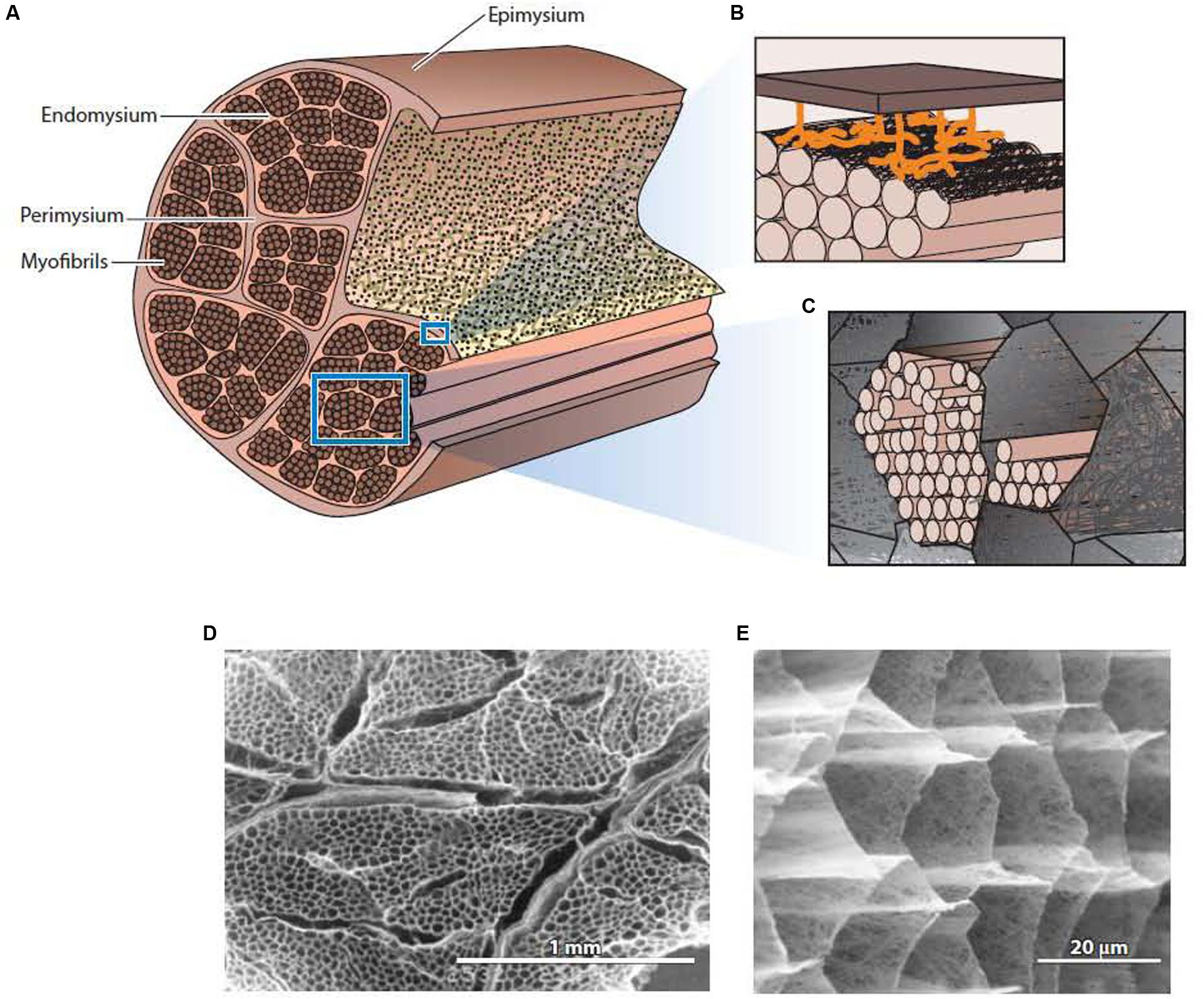



Frontiers The Structure And Role Of Intramuscular Connective Tissue In Muscle Function Physiology
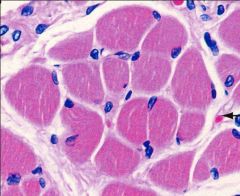



Histology Exam I Part 2 Flashcards Cram Com




Muscle Histology Prelab
コメント
コメントを投稿